Cannabis is one of the most widely consumed products in the world. The high it gives after consumption is highly sought after for recreational as well as therapeutic relief. The mind-altering effects of marijuana, aka, cannabis, have wide applications in the world of medicine, finding use in treating multiple neurological disorders like anxiety, epilepsy, sleep disorders like insomnia, apnea and even in some cancer-related symptoms. There are benefits of using CBD but the key is the endocannabinoid system within the human body.
However, have you ever wondered why cannabis has the effect it does on our minds and body? What makes it so influential that it alters the mind and relieves chronic pain symptoms? This is because our body has an inherent ability to interact with cannabis and its elements, including cannabidiol (CBD) and THC (the compound that produces the famous high).
This ability is channeled through our body’s endocannabinoid system. It actively interacts with both the psychoactive and the non-psychoactive elements of cannabis to not only make us experience the high but also the medicinal relief. It regulates the internal biology and works with cannabis to effectively sustain its positive effects.
Table of Contents
What Is The Endocannabinoid System?
One of the most peculiar parts of our biological composition, the endocannabinoid system (ECS) that plays a vital role in maintaining and regulating several processes inside the body. It interacts with the brain receptors and helps in maintaining homeostasis (our physical and chemical equilibrium). It is essentially a cell-signalling system that was discovered by scientists while researching about THC. A relaxed body can use CBD to sleep and have less anxiety using CBD
The word endocannabinoid is a portmanteau of ‘cannabinoid’ and ‘endogenous’. Endogenous means that it is created inside the body naturally without any external stimulus. Therefore, the ECS is functional even if the body is not consuming cannabis and endocannabinoid enzymes are essentially substances that are naturally produced inside the body.
The endocannabinoid system constitutes of three parts:
- Endocannabinoids
- Receptors
- Enzymes
The receptors are found in the nervous system as well as in other parts of the body and interact with the endocannabinoids and the cannabinoids. The metabolic enzymes work to break down the endocannabinoids and cannabinoids.
Endocannabinoids are naturally produced in the body and the ECS is one of the most important parts of the body. It is responsible for efficiently regulating the effects of marijuana, specifically THC and CBD compounds.
Homeostasis and how it relates to the ECS
To get a complete understanding of the endocannabinoid system, it’s crucial to first understand the meaning and concept of homeostasis.
Homeostasis is the process through which the body maintains its most optimal function. It is the way through which the internal biological environment remains stable and regulated and defends against the external environment. It’s basically like an analytics tool that informs the analyst whether all parameters are performing to their most optimum level and normalcy is maintained.
The easiest way to understand this is to know that the human body works round the clock to monitor and maintain the normal levels of all enzymes and hormones, which ultimately help in keeping the internal systems in the right place. This is similar to how any electronic or automobile function — the internal components work to ensure that all parts are performing the way they should so that the final output is perfect. Therefore, the internal temperature, the hormones, the heart rate, stamina, blood flow and other parameters are all regulated through homeostasis to tell the body whenever any of these go in the wrong direction and spoil the balance.
In case any of these metrics go off balance, the endocannabinoid system comes into force to stabilize the imbalance. For example, if your body gets heated up a lot, the ECS helps in bringing down the temperature. Therefore, the ECS is vital in maintaining homeostasis and keeping the cells of the body in their normal zone. If it gets dysfunctional, the body’s internal functioning can go haywire which can get extremely dangerous.
How it does this is what we will explore in the next section.
How Does The Endocannabinoid System Work?
The three core components of the endocannabinoid system work together to maintain the internal functioning of the body and interact with CBD. Many people with skin conditions like acne will find CBD to be a cure.
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids, the molecules produced by the body itself, are endogenous cannabinoids that help regulate the internal systems. These are produced by the body as per the requirements and there is no fixed quantity that’s created. These cannabinoids work to bind the receptors as is done by the cannabinoids produced by the cannabis plants.
Two endocannabinoids are currently known to scientists — anandamide also called as AEA, and 2-arachidonoylglyerol, also called as 2-AG. These endogenous cannabinoids are made from the molecules created by the body cells whenever there is an imbalance in the body. Unlike other molecules, that are created anyway and are stored in the body for use, these endocannabinoids are created only when there is a demand for them.
Cannabinoid receptors
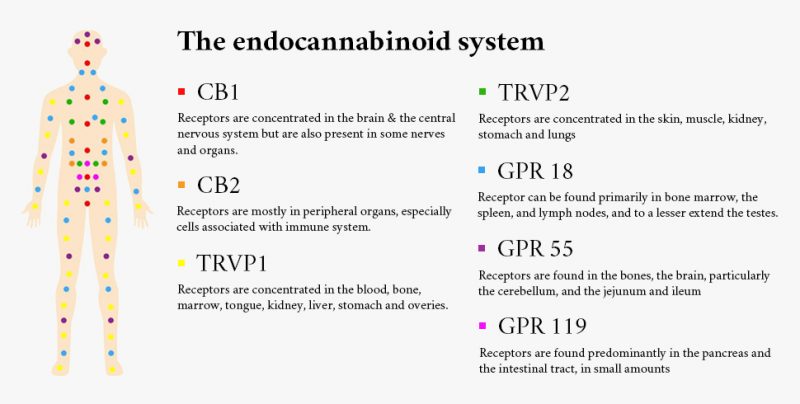
Cannabinoid receptors are neurological receptors that are found throughout the body. These receptors stay on the cell surface and monitor the environment of the body external to the cells, passing on the information to the membrane to revert with the right response and create the necessary molecules to restore the normal conditions. CB1 and CB2 are the two main cannabinoid receptors, though not the only ones.
CB1 receptors are the ones that interact with the psychoactive compound, THC and convey the mind-altering effect of getting high. These are primarily found inside the brain. On the other hand, the CB2 receptors are mainly found outside the brain, mostly in the immune system. The CB1 and CB2 receptors are bonded by endocannabinoids and stimulate the ECS.
Metabolic Enzymes
Metabolic enzymes have the responsibility to break down the endocannabinoids and destroy them once they served their purpose. The main metabolic enzymes are fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), responsible for breaking down AEA, and monoacylglycerol acid lipase which is responsible for breaking down 2-AG. The main purpose of these enzymes is to ensure that endocannabinoids do not stay in the body for longer than needed.
Therefore, these three components of the ECS work together to maintain homeostasis and restoring any imbalance in the body and also inducing the high or the relief that’s experienced after consuming cannabis.
Endocannabinoid Deficiency
With more and more research about the endocannabinoid system, it has also been revealed that the system in itself can be dysfunctional. These cases, where ECS dysfunctions, are studied together under the term clinical endocannabinoid deficiency (CECD).
This is an umbrella term under which all conditions related to the dysfunctioning of the endocannabinoid system are studied. Some of the conditions include disorders and illnesses like migraines, fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome and others. The problem here is that these illnesses also referred to as central sensitivity syndromes are naturally resistant to treatments in general and affect more than just one part of the body.
On the outside, it can seem unrelated, the systems that these disorders affect. For instance, in the case of fibromyalgia, the areas affected include the immune system, the endocrine system, the digestive system as well as the nervous system, which appears to have no correlation until the ECS and the body’s ability to maintain normal functions, i.e. homeostasis, is taken into consideration.
Therefore, to treat these conditions, much more research is needed into the use of cannabinoids since the symptoms and the areas affected, point in the direction of using CBD for their treatment.
What Are The Functions Of The Endocannabinoid System
There are several functions of the endocannabinoid system, the main being to maintain homeostasis. A lot of other things get affected by the functioning of ECS, including appetite, memory, inflammation of the immune system, metabolism and motor control as well.
A host of other functions that get regulated by ECS all contribute together to enable the body to remain in homeostasis. Therefore, the main function of ECS is to keep the internal environment of the body stable and secrete the metabolic enzymes or the endocannabinoids as and when the need arises.
CBD and The Endocannabinoid System
CBD is one of the complex compounds extracted from cannabis, the hemp plant. Unlike THC, CBD is completely non-psychoactive and does not make you high nor does it have any dangerous effects on the body and the mind. CBD works a little differently than the THC and how it interacts with the ECS.
CBD interacts with the overall levels of endocannabinoids and does not bind with CB1 or CB2 receptors in particular. It prevents the FAAH enzyme from getting created and thus causes the levels of anandamide to go up since FAAH is responsible for destroying anandamide. This results in increasing the endocannabinoid tone and thus, decreasing the anxiety levels. FAAH, in studies, has been known to increase anxiety and inhibiting it offers relief to the people suffering from the disorder.
THC and The Endocannabinoid System
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the main cannabinoid compound extracted from cannabis and is responsible for giving people the marijuana high. THC interacts with ECS by binding to the CB1 receptors found in the brain. It can also bind itself to the CB2 receptors found all over the body and thus has a high influence on the mind as well as the body. The metabolic enzymes are not capable of breaking down THC that easily, which helps it in being retained in the body for longer than necessary.
THC, on interacting with the endocannabinoid system, can cause anxiety as well as pain relief. There are studies ongoing to decipher the impact.
The important decision is to find the best CBD oil UK shops using reputable CBD isolate wholesale suppliers or reputable established CBD whitelabel UK companies.
In Conclusion
The endocannabinoid system is a vital component of the internal body that helps in keeping everything normal. The components of ECS interact with the external cannabinoids to incite the positive or the negative functions, depending on the cannabinoid consumed. It is responsible for the high that THC gives and the pain relief that’s induced by CBD. There is a lot more research that needs to be done in the area to understand the complexity of ECS and use it to better treat illnesses like sleep disorders, chronic pain, anxiety and even cancer.